Battle of Trocadero
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2021) |
| Battle of Trocadero | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Spanish Expedition | |||||||
 French nocturnal decisive assault on Fort Trocadero, on the night of 30 and the day of 31 August 1823 (by P. Delaroche, Chateau de Versailles) | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 30,000 soldiers | 1,700 soldiers | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
31 dead 110 wounded |
150 dead 300 wounded 1,000 captured | ||||||
The Battle of Trocadero, fought on 31 August 1823, was the only significant battle in France's expedition in support of the Spanish King Ferdinand VII.[dubious – discuss] The French defeated the Spanish liberal forces and restored Ferdinand to absolute rule.
Prelude
[edit]After the downfall of Napoleon, King Ferdinand VII of Spain refused to adopt the liberal Spanish Constitution of 1812 and in 1820 faced a rebellion in favour of a constitutional monarchy, led by Rafael del Riego y Nuñez. The King was captured and detained at Cádiz, the seat of the Spanish parliament, the Cortes. Alarmed by these events, the other European powers convened in October 1822 at the Congress of Verona and authorized France to intervene in the conflict and restore the rule of Ferdinand, with only Britain abstaining from that decision.
Military intervention
[edit]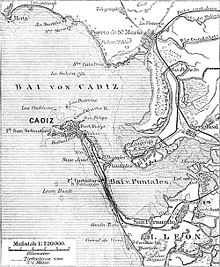
On 17 April 1823, French forces led by Louis-Antoine, Duke of Angoulême, son of the future Charles X, crossed the Pyrenees into Spain.
The French forces were welcomed by the Basques and conservative Spaniards. The duke dispatched a force to besiege San Sebastián while he launched an attack on Madrid, held by the rebel government, which on 23 May withdrew to Seville. Madrid's military commander secretly surrendered and fled to France, and the leaderless Madrid garrison could not keep out the French, who seized the city and installed a regent, pending Ferdinand's expected return.[2]
The French moved south to deal with the rebels at Cádiz, and besieged the fort of Trocadero, which controlled access to the city. On 31 August 1823 they launched a surprise bayonet attack from the sea side, taking advantage of the low tide, and took the fort. After this action, French infantry captured the Trocadero village by a flank attack. After this last action, 1700 Spanish soldiers were captured by the French.
Cádiz itself held out for three weeks despite bombardments, but was forced to surrender on 23 September 1823 and King Ferdinand was released and handed over to the French. Despite a prior promise of amnesty, the king ordered reprisals against the rebels; in the following years, an estimated 30,000 people were executed and 20,000 imprisoned.[citation needed]
Aftermath
[edit]
The Battle of Trocadero was one of the events that prompted U.S. President James Monroe to proclaim what would become known as the Monroe Doctrine on 2 December 1823, to safeguard the Americas against intervention by European powers.[3]
The fall of Trocadero was commemorated in Paris, with the Trocadéro, where the city was expanding to the edges of the Bois de Boulogne. Louis-Antoine, Duke of Angoulême, the victor of the battle, was offered the title "Prince of Trocadero" by the Spanish king, but he refused to accept it, partly in disgust at Ferdinand going back on his promises of clemency.
In Les Misérables, Victor Hugo devoted several paragraphs to the battle (Volume II, Book 2, chapter 3), in which he called the battle "a fine military action", but also said that "[t]he war of 1823 was an outrage on the generous Spanish nation, (..) at the same time, an outrage on the French Revolution."
See also
[edit]- Siege of Pamplona (1823), one of the other major actions of the war
References
[edit]- ^ A. G. MacDonell (2015). Napoleon and his Marshals. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. ISBN 978-1516853144.
- ^ Kohn, George Childs (2013). Dictionary of wars. Oxon, England: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-315-06296-9. OCLC 897454971.
- ^ Morison, S. E. (1924). "The Origin of the Monroe Doctrine, 1775-1823". Economica (10). JSTOR: 27–51. doi:10.2307/2547870. ISSN 0013-0427. JSTOR 2547870.
External links
[edit]- Le Temps des Révolutions Conquest of Trocadero (in French)
- Cadiz 1823, el año del terror Cadiz 1823, the year of terror (in Spanish)
- Französische Invasion in Spanien 1822/23 Archived 8 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine French invasion of Spain 1822/23 (in German)
- Victor Hugo, Les Misérables, Volume II, Book 2, chapter 3 (in English)
