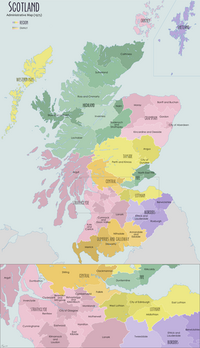
Ross and Cromarty
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2022) |
| Ross and Cromarty Ros agus Cromba (Scottish Gaelic) | |
|---|---|
| Historic county | |
 Ross and Cromarty: county (1889–1975) | |
| Area | |
| • Coordinates | 57°40′N 5°00′W / 57.667°N 5.000°W |
Ross and Cromarty (Scottish Gaelic: Ros agus Cromba), is an area in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. In modern usage, it is a registration county and a lieutenancy area. Between 1889 and 1975 it was a county.
Historically, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire were separate counties, with Cromartyshire comprising a number of disconnected tracts of land scattered across Ross-shire. The two counties shared a sheriff from 1748, and were both included in the Ross and Cromarty constituency from 1832. They were formally united into a single county called Ross and Cromarty in 1889.
The mainland part of the county had a coast to the east onto the Moray Firth, and a coast to the west onto the Minch. Much of the mainland is sparsely populated, including parts of the Northwest Highlands mountains, with its main towns all being on the east coast, including Dingwall (the county town), Alness, Cromarty, Fortrose, Invergordon and Tain. The county also covered parts of the Outer Hebrides, principally the Isle of Lewis, including the town of Stornoway. The neighbouring counties were Sutherland to the north and Inverness-shire to the south.
The county ceased to be used for local government purposes in 1975. Since then, the mainland has been part of the Highland region, which became a single-tier council area in 1996. The Outer Hebrides parts of the county became part of the Western Isles, which since 1998 has used only the Scots Gaelic version of its name, Na h-Eileanan an Iar. The pre-1975 county boundaries are still used for certain functions, being a registration county. There was a local government district called Ross and Cromarty from 1975 to 1996, which was a lower-tier district within the Highland region, covering most but not all of the mainland part of the pre-1975 county.
The Ross and Cromarty lieutenancy area, which prior to 1975 had been the county, was redefined in 1975 to be the Ross and Cromarty district plus the neighbouring Skye and Lochalsh district. The registration county and lieutenancy area therefore have slightly different definitions. Notable differences are that the registration county includes the Isle of Lewis and Kincardine, which are not in the lieutenancy area, whereas the lieutenancy area includes the Isle of Skye, which is not in the registration county. The lieutenancy area is 8,019 square kilometres (3,096 square miles) in extent.
History
[edit]Before 1889
[edit]The mainland part of Ross and Cromarty broadly corresponds to the ancient province of Ross. This area was claimed by the Scottish crown from 1098, having previously been under Norwegian overlordship. It was initially included within the shire of Inverness following its incorporation into Scotland.[1]
By the mid-13th century there were sheriffs based at Cromarty and Dingwall, both within the province of Ross, but each appears to have had only a small area of jurisdiction around those towns, rather than the larger territories usually given to sheriffs. The Sheriff of Inverness was therefore still responsible for most of Ross. The position of Sheriff of Dingwall did not endure.[2] After a couple of abortive attempts, the rest of Ross was eventually separated from Inverness-shire in 1661, being given its own Sheriff of Ross and becoming Ross-shire.[3]

The interests of landowners led to some variations in the 1661 definition of Ross-shire from the old province of Ross. In particular, the Isle of Lewis had not been in Ross but was included in Ross-shire on account of being owned by Kenneth Mackenzie, 3rd Earl of Seaforth, a major landowner in Ross. Conversely, an area north of the River Beauly including Beauly and Kilmorack had been in Ross but was excluded from Ross-shire on account of being owned by Clan Fraser of Lovat, based in Inverness-shire. Likewise the Ferintosh estate on the Black Isle was made an exclave of Nairnshire on account of being owned by the Forbes family. The small shire of Cromarty (which still just covered that town and its immediate vicinity) retained its independence.[4][5] Cromartyshire was significantly enlarged in the late 17th century to gain numerous separate tracts of land scattered across Ross-shire which were owned by George Mackenzie, Viscount of Tarbat, who owned the barony of Cromarty.[6][7][8][9]
Following the Jacobite rising of 1745, the government passed the Heritable Jurisdictions (Scotland) Act 1746, returning the appointment of sheriffs to the crown in those cases where they had become hereditary positions, as had been the case for the Sheriff of Cromarty.[10] The scope for a major landowner or clan chief to control the office of sheriff, which had been the major cause of Cromartyshire being separated from Ross-shire, was therefore greatly reduced. From 1748 the government merged the positions of Sheriff of Ross and Sheriff of Cromarty into a single position.[11]
Despite sharing a sheriff from 1748, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire remained legally separate counties. They retained separate Commissioners of Supply (established in 1667),[12][13] and from 1794 each appointed their own lord-lieutenants. From 1860 the commissioners of supply for the two counties were directed to work together on delivering some functions, notably relating to prisons.[14]
County
[edit]
The county of Ross and Cromarty was created under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, covering the combined area of the two former counties of Ross-shire and Cromartyshire. The new county came into being on the passing of the act on 26 August 1889, from when the previously separate commissioners of supply for each former county merged into a single body, and the last Lord Lieutenant of Ross-shire, Kenneth Smith Mackenzie, became the first Lord Lieutenant of Ross and Cromarty.[15]
The act also established elected county councils, which came into effect in 1890, taking over most of the functions of the commissioners (which were eventually abolished in 1930). The new Ross and Cromarty County Council held its first official meeting on 8 May 1890 at Dingwall Sheriff Court, which had been built in the 1840s as the main courthouse for Ross-shire and had also served as the meeting place for the commissioners. Kenneth Smith Mackenzie, already the lord lieutenant and a major landowner in the county, was also appointed the first convener of the county council.[16][17]

The act also led to a review of boundaries, with exclaves being transferred to a county they actually bordered, and parish and county boundaries being adjusted to eliminate cases where parishes straddled county boundaries. The main exclaves in the area prior to the act had been the many parts of Cromartyshire scattered across Ross-shire, which were resolved as a result of the two counties merging into one. After the merger, there still remained an exclave of Nairnshire at the Ferintosh estate on the Black Isle, whilst the parish of Urray straddled Inverness-shire and Ross and Cromarty. Ferintosh was transferred to Ross and Cromarty, and the parts of Urray in Inverness-shire were transferred to the Inverness-shire parish of Kilmorack. These boundary changes (and others to eliminate exclaves in parish boundaries) took effect in 1891.[18]
Despite the creation of Ross and Cromarty in 1889, the Royal Mail used 'Ross-shire' as the name of the postal county for the mainland part of Ross and Cromarty, including the parts which had been in Cromartyshire.[19] Postal counties were officially discontinued in 1996.
Ross and Cromarty County Council built itself a new headquarters at County Buildings in Dingwall in 1965.[20]
Since 1975
[edit]Local government was reformed in 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, which replaced Scotland's counties, burghs and landward districts with a two-tier structure of upper-tier regions and lower-tier districts for most of Scotland. A single-tier structure of island areas was used for Orkney, Shetland and the Western Isles. The mainland of Ross and Cromarty became part of the Highland Region, whilst the Outer Hebrides parts (the landward district of Lewis and burgh of Stornoway) became part of the Western Isles.[21][22]
The part of Ross and Cromarty which went to the Highland region was split between three lower-tier districts.[21][23][24]
- Ross and Cromarty district, covering most of the mainland of the pre-1975 county, and the nearby islands that were not transferred to the Western Isles.
- Skye and Lochalsh district, covering the Isle of Skye district from Inverness-shire plus the South West District from Ross and Cromarty (comprising the parishes of Glenshiel, Kintail, and Lochalsh).
- Sutherland district, covering most of the pre-1975 county of Sutherland, plus the parish of Kincardine from Ross and Cromarty.
As part of the 1975 reforms, the last lord lieutenant of the county of Ross and Cromarty, Alexander Francis Matheson, became lord lieutenant of the new Ross and Cromarty lieutenancy area, which was defined as the combined area of the new Ross and Cromarty district plus the Skye and Lochalsh district.[25]
The Ross and Cromarty District Council was based at the former county council's headquarters at County Buildings in Dingwall.[26] Throughout the district's existence from 1975 to 1996, a majority of the seats were held by independent councillors.[27]
Further local government reforms in 1996 under the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 saw the regions and districts created in 1975 abolished and replaced with single-tier council areas. The former Highland region became one of the new council areas.[28] The lieutenancy areas continue to be defined as they had been in 1975 despite the abolition of the districts on which they were based.[29] The boundaries of the historic county of Ross and Cromarty (as it was following the 1891 boundary changes) are still used for some limited official purposes connected with land registration, being a registration county.[30]
In 1998 the Western Isles Council formally changed the English language version of the area's name from Western Isles to Na h-Eileanan an Iar (Scots Gaelic for 'Western Isles'), to be used in both English and Gaelic contexts.[31]
Geography
[edit]
Western Ross and Cromarty, also known as Wester Ross, is typified by its mountainous Highland scenery, especially the Torridon Hills which includes such peaks as Beinn Eighe and Liathach. The highest point in the county is Càrn Eighe at 1,183 metres (3,881 feet). It contains a long, fractured coastline along The Minch and Inner Sound (opposite Skye), consisting of a number of isolated peninsulas split by sea lochs; from north to south the chief of these are Coigach, Loch Broom, the Scoraig peninsula, Little Loch Broom, Gruinard Bay, Rubha Mòr peninsula, Loch Ewe, Rua Reidh/Melvaig peninsula, Loch Gairloch, Loch Torridon, Applecross peninsula, Loch Kishorn, Loch Carron, Lochalsh peninsula, Loch Long, Loch Duich and the Glenelg peninsula which is shared with Inverness-shire.
The eastern half (Easter Ross) is generally flatter, and consists of towns, villages and farmland bordering the Moray Firth. In the north Dornoch Firth separates the county from Sutherland; near the Dornoch Firth Bridge lies the thin, tapering Ness of Portnaculter peninsula. In the north-east can be found the hammerhead-shaped Tarbat peninsula; across Cromarty Firth lies the Black Isle (actually a peninsula not an island). To the south-east Beauly Firth forms the border with Inverness-shire.
The county contains numerous lochs, the most prominent of these being Loch Ailsh, Crom Loch, Loch a' Choire Mhòir, Loch Fada, Lochan Gaineamhaich, Loch Cluanie, Loch Loyne, Loch Monar, Loch Mullardoch, Loch a' Bhealaich, Loch nan Eun, Loch na Leitreach, Loch an Laoigh, Loch Calavie, An Gead Loch, Loch an Tachdaidh, Loch Sgamhain, Loch a' Chroisg, Loch Clair, Loch Coulin, Loch Fhiarlaid, Loch Dughaill, Loch Coultrie, Loch Damph, Loch Lundie, Loch na A-Oidhche, Loch Maree, Loch a' Ghodhainn, Loch Ghaineamhach, Loch Bad an Sgalaig, Loch a' Bhraoin, Loch Fannich, Fionn Loch, Loch na Sealga, Loch Eye, Loch Glass, Loch Morie, Loch Ussie, Loch Achilty, Loch Garve, Loch Luichart, Loch Achanalt, Loch Meig, Loch Droma, Loch Glascarnoch, Loch Coire Làir, Loch Vaich, Loch a' Chaorunn, Loch na Caoidhe, Loch Beannacharain, Loch na Totaig, Loch Osgaig, Loch Raa, Loch Vatachan, Fionn Loch, Loch Veyatie, Loch Lurgainn, Loch Bad a' Ghaill, Loch Sionascaig, Lochan Tuath, Loch an Doire Duibh, Loch Doire na h-Airbhe, Loch a Ghille, Loch Buine Mhòire, Loch Call an Uidhean, Loch a' Chroisg, Loch Achall, Loch an Daimh, Loch na Maoile, Loch Ob an Lochain, Clar Lochan, Loch an Eilein and the Orrin Reservoir.
Lewis is the northern part of Lewis and Harris, the largest island of the Outer Hebrides and the third largest in the British Isles after Britain and Ireland. Due to its flatter, more fertile land, Lewis contains three-quarters of the population of the Western Isles, and the largest settlement, Stornoway. To the west lie the isolated and uninhabited Flannan Isles. About 44 miles (71 kilometres) north of the Butt of Lewis lie North Rona and Sula Sgeir, a remote group of islands which are included within Ross-shire.
Islands
[edit]Mainland
[edit]- A' Ghlas-Leac
- An Garbh-Eilean
- Black Islands
- Crowlin Islands
- Eilean a' Chait
- Eilean a' Mhal
- Eilean an Inbhire Bhàin
- Eilean an t-Sratha
- Eilean Bàn
- Eilean Chuaig
- Eilean Dubh Dhurinis
- Eilean Furadh Mòr
- Eilean Horrisdale
- Eilean Mòineseach
- Eilean Mòr
- Eilean na Bà
- Eilean na Bà Mòr
- Eilean na Beinne
- Eilean na Creige Duibhe
- Eilean nam Feannag
- Eilean nan Naomh
- Eilean Stacan
- Eilean Tioram
- Eileanan Dubha
- Fraoch Eilean
- Fraoch Eilean Mòr
- Fraoachlan
- Glas Eilean
- Green Island
- Gruinard Island
- Isle of Ewe
- Kishorn Island
- Làrach Tigh Mhic Dhomhnuill
- Longa Island
- Sgeir a' Bhuic
- Sgeir a' Ghair
- Sgeir an Araig
- Sgeir an Fheòir
- Sgeir Bhuide
- Sgeir Bhuidhe
- Sgeir Chreagach
- Sgeir Dùghaill
- Sgeir Fhada
- Sgeir Ghlas
- Sgeir Maol Mhoraidh
- Sgeir Maol Mhoraidh Shuas
- Sgeir Mhòr
- Sgeir na Trian
- Shieldaig Island
- Strome Islands
- Summer Isles
- Ulluva
Lewis
[edit]- Àird Orasaigh
- Bearasaigh
- Bhuaile Mhòr
- Bràighe Mòr
- Bratanais Mòr
- Campaigh
- Ceabagh
- Ceabhaigh
- Cealasaigh
- Cliatasaigh
- Craigeam
- Cruitear
- Cùl Campaigh
- Eilean a' Bhlàir
- Eilean an Tighe
- Eilean Àrnol
- Eilean Beag a' Bhàigh
- Eilean Bhàcasaigh
- Eilean Bhinndealaim
- Eilean Chearstaigh
- Eilean Chalaibrigh
- Eilean Chaluim Cille
- Eilean Cheòis
- Eilean Dubh a' Bhàigh
- Eilean Fir Chrothair
- Eilean Liubhaird
- Eilean Mhealasta
- Eilean Molach
- Eilean Mòr a' Bhàigh
- Eilean Mòr Lacasaidh
- Eilean Mòr Phabail
- Eilean nan Uan
- Eilean Orasaidh
- Eilean Orasaigh
- Eilean Rosaidh
- Eilean Sgarastaigh
- Eilean Shìophoirt
- Eilean Teinis
- Eilean Thinngartsaigh
- Eilean Thòraidh
- Eilean Thuilm
- Eilean Trosdam
- Eughlam
- Eunaigh Mòr
- Flannan Isles
- Fleisgeir
- Flodaigh, Lewis
- Flodaigh (Outer Loch Ròg)
- Fuaigh Beag
- Fuaigh Mòr
- Garbh Eilean
- Geile Sgeir
- Glas Sgeir
- Gousam
- Great Bernera
- Grèineam
- Hairsgeir Beag
- Hairsgeir Mòr
- Lada Sgeir
- Langaisgeir Mòr
- Lewis (part of the larger Lewis and Harris island)
- Linngeam
- Liongam
- Lìth Sgeir
- Little Bernera
- Màs Sgeir
- Pabaigh Beag
- Pabaigh Mòr
- Riosaigh
- Seanna Chnoc
- Sgeir a' Mhurain
- Sgeir Dhail
- Sgeir Dhearg
- Sgeir Ghlas Bheag
- Sgeir Ghobhlach
- Sgeir Leathann
- Sgeir Liath
- Sgeir Mhòr Shildinis
- Sgeir Mol Srupair
- Sgeir Sgianailt
- Sgeir Tanais
- Sgeirean An Arbhair
- Shiant Islands
- Siaram Bostadh
- Siaram Mòr
- Tabhaigh Bheag
- Tabhaigh Mhòr
- Tamna
- Tanaraigh
- Tannaraidh
- Thalta Sgeir
- Vacsay (Bhàcasaigh in Gaelic)
North Rona
[edit]- Ghealldraig Mhòr
- Gralisgeir
- Lisgear Mhòr
- North Rona
- Sula Sgeir
- Thamna Sgeir
-
Eilean Bàn from the Skye Bridge, looking towards Kyle of Lochalsh
-
Shag birds on Longa Island
-
The Isle of Ewe
-
Cave on Garbh Eilean, Shiant Isles
-
The famous Callanish Stones on Lewis
-
Seana Chnoc (at left) and Bearasaigh from the south west. Stac nam Balg is just visible to the left of Seanna Chnoc
Economy and population
[edit]The main economic activities in Ross and Cromarty are crofting, fishing and tourism. The population as of 2001 was 49,967.[32]
Parliamentary constituency
[edit]The name Ross and Cromarty was first used for the Ross and Cromarty county constituency of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1832 to 1983. As created in 1832, the constituency merged two former county constituencies: the Ross-shire constituency and the Cromartyshire constituency, and it elected a Member of Parliament to represent the counties of Ross-shire and Cromartyshire, minus their parliamentary burghs, Dingwall, Tain and Fortrose, which were represented as components of the Wick burghs constituency and the Inverness burghs constituency.
Constituency boundaries were altered in 1918, by the Representation of the People Act 1918, and the Ross and Cromarty constituency acquired the boundaries of the county of Ross and Cromarty, including the former parliamentary burghs, but minus Stornoway and Lewis, which became part of a new constituency, the Western Isles constituency.
In 1983, the Ross, Cromarty and Skye constituency was created to represent the then Ross and Cromarty district and Skye and Lochalsh district. The Kincardine area joined the Caithness and Sutherland constituency.
Civil parishes
[edit]Parishes existed from medieval times. From 1845 to 1894 they had parish boards and from 1894 to 1930 they had parish councils. They have had no administrative functions since 1930, but continue to be used for the presentation of statistics.
Following the 1891 boundary changes, the county of Ross and Cromarty contained the following civil parishes:[22][23]
- Alness
- Applecross
- Avoch
- Barvas (on Lewis)
- Contin
- Cromarty (included burgh of same name)
- Dingwall (included burgh of same name)
- Edderton
- Fearn
- Fodderty
- Gairloch
- Glenshiel
- Killearnan
- Kilmuir Easter
- Kiltearn
- Kincardine
- Kintail
- Knockbain
- Lochalsh
- Lochbroom
- Lochcarron
- Lochs (on Lewis)
- Logie Easter
- Nigg
- Resolis
- Rosemarkie (included burgh of Fortrose)
- Rosskeen (included burgh of Invergordon)
- Stornoway (included burgh of same name, on Lewis)
- Tain (included burgh of same name)
- Tarbat
- Uig (on Lewis)
- Urquhart and Logie Wester
- Urray
Transport
[edit]
The Kyle of Lochalsh railway line traverses the county west–east, terminating at Inverness. The Far North Line goes north–south along the east coast, connecting Inverness in the south with Thurso and Wick in the north.
The Black Isle is connected by bridge to the 'mainland' - Cromarty Bridge in the north-west and the Kessock Bridge in the south-west. At the tip of the peninsula a ferry provides access to the Tarbat peninsula. The Skye Bridge links Kyle of Lochalsh to the isle of Skye.
Various buses operated by Stagecoach Group link the major towns of the east coast, with the 61 bus connecting Ullapool to Inverness.[33] The latter route is also served by Scottish Citylink in the summer, continuing on to Glasgow.[34] Various independent bus companies link the smaller towns of Wester Ross, though online information is limited.
A ferry connects Stornoway on Lewis with Ullapool on the mainland, taking about three hours.
The county contains one airport - Stornoway - which provides passenger flights to destinations within Scotland as well as London Southend.
Settlements
[edit]Mainland
[edit]


- Achnasheen
- Achiltibuie
- Alness
- Altandhu
- Applecross
- Ardgay
- Aultbea
- Avoch
- Badenscallie
- Balintore
- Barbaraville
- Conon Bridge
- Contin
- Cromarty
- Culbokie
- Culrain
- Diabaig
- Dingwall
- Dornie
- Dundonnell
- Edderton
- Evanton
- Fearn
- Fortrose
- Garve
- Gairloch
- Hill of Fearn
- Inver
- Invergordon
- Inverinate
- Inverness
- Jemimaville
- Kildary
- Kilmuir, Black Isle
- Kilmuir, Easter Ross
- Kinlochewe
- Kyle of Lochalsh
- Laide
- Lochcarron
- Marybank
- Maryburgh
- Milton
- Muir of Ord
- Mulbuie
- Munlochy
- Nigg
- North Kessock
- Polbain
- Polglass
- Poolewe
- Portmahomack
- Reraig
- Rieff
- Rosemarkie
- Shieldaig
- Strathcarron
- Strathpeffer
- Stromeferry
- Tain
- Torridon
- Ullapool
Isle of Lewis
[edit]
- Achmore
- Adabrock
- Aignish
- Aird
- Aird Uig
- Airidhbhruaich
- Arnol
- Back
- Balallan
- Ballantrushal
- Barvas
- Borve
- Bragar
- Branahuie
- Brue
- Breaclete
- Breanish
- Breasclete
- Calbost
- Callanish
- Carishader
- Carloway
- Caverstay
- Cliff
- Coll
- Cromore
- Cross
- Crossbost
- Crowlista
- Dalbeg
- Eagleton
- Eorodale
- Eoropie
- Fivepenny
- Flesherin
- Garynahine
- Garyvard
- Geishader
- Gisla
- Gravir
- Gress
- Grimshader
- Habost
- Hacklete
- Holm
- Islivik
- Keose
- Keose Glebe
- Kershader
- Kirkibost
- Kneep
- Knockaird
- Laxay
- Laxdale
- Lemreway
- Leurbost
- Lionel
- Lower Bayble
- Mangursta
- Marvig
- Marybank
- Meavik
- Melbost
- Newmarket
- Newvalley
- North Dell
- North Galson
- North Tolsta
- Orinsay
- Parkend
- Plasterfield
- Portnaguran
- Port of Ness
- Portvoller
- Ranish
- Sandwick
- Shader
- Shawbost
- Sheshader
- Shieldenish
- Shulishader
- Skigersta
- South Dell
- South Galson
- Steinish
- Stornoway
- Swainbost
- Timsgarry
- Tobson
- Tong
- Upper Bayble
- Valtos
See also
[edit]- Ross, Scotland
- Shires of Scotland
- List of counties of Scotland 1890–1975
- Medieval Diocese of Ross
- Politics of the Highland council area
References
[edit]- ^ Grant, Alexander (2000). "The Province of Ross and the Kingdom of Alba". In Cowan, Edward J.; McDonald, R. Andrew (eds.). Alba: Celtic Scotland in the Middle Ages. East Linton: Tuckwell Press. pp. 98–110. ISBN 1 86232 151 5. Retrieved 28 August 2024.
- ^ Taylor, Alice (2016). The Shape of the State in Medieval Scotland, 1124–1290. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 144, 234–235. ISBN 9780198749202. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ Kennedy, Allan D. (2014). Governing Gaeldom: The Scottish Highlands and the Restoration State, 1660-1688. Brill. pp. 155–156. ISBN 9789004269255. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ Brown, Keith. "Act anent the shire of Ross". The Records of the Parliament of Scotland to 1707. University of St Andrews. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ MacKenzie, George Steuart (1810). A General View of the Agriculture of the Counties of Ross and Cromarty. London: Richard Phillips. pp. 3–4. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ Brown, Keith. "Act dissolving the barony of Tarbat from the shire of Ross, 4 June 1685". Records of the Parliament of Scotland. University of St Andrews. Retrieved 6 September 2024.
- ^ Brown, Keith. "Act in favours of my lord advocat, 4 June 1685". Records of the Parliament of Scotland. University of St Andrews. Retrieved 6 September 2024.
- ^ Brown, Keith. "Act in favour of [George MacKenzie], viscount of Tarbat, 19 July 1690". Records of the Parliament of Scotland. University of St Andrews. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ Mackenzie, George Steuart (1810). General View of the Agriculture of the Counties of Ross and Cromarty. pp. 15–19. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ Whetstone, Ann E. (1977). "The Reform of the Scottish Sheriffdoms in the Eighteenth and Early Nineteenth Centuries". Albion: A Quarterly Journal Concerned with British Studies. 9 (1): 61–71. doi:10.2307/4048219. JSTOR 4048219.
- ^ Sheriffs (Scotland) Act 1747
- ^ Brown, Keith. "Act of the convention of estates of the kingdom of Scotland etc. for a new and voluntary offer to his majesty of £72,000 monthly for the space of twelve months, 23 January 1667". Records of the Parliament of Scotland. University of St Andrews. Retrieved 25 February 2023.
- ^ "Scottish Counties and Parishes: their history and boundaries on maps". National Library of Scotland. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- ^ A Collection of the Public General Statutes. 1860. p. 784. Retrieved 6 September 2024.
- ^ Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict. c. 50) Section 39. 1889. p. 228. Retrieved 10 September 2024.
- ^ Historic Environment Scotland. "Dingwall Sheriff Court including former police station, prison, gatepiers and railings, Ferry Road, Dingwall (LB24500)". Retrieved 10 September 2024.
- ^ "First meeting of Ross-shire County Council - yesterday". Ross-shire Journal. Dingwall. 9 May 1890. p. 3. Retrieved 10 September 2024.
- ^ Shennan, Hay (1892). Boundaries of counties and parishes in Scotland as settled by the Boundary Commissioners under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889. Edinburgh: W. Green. p. 132. Retrieved 10 September 2024.
- ^ Post Office Guide. 1911. p. 245. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- ^ "Public urged to attend Dingwall meeting". Ross-shire Journal. 28 October 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ a b "Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, 1973 c. 65, retrieved 17 April 2023
- ^ a b "Quarter-inch Administrative Areas Maps: Scotland, Sheet 2, 1968". National Library of Scotland. Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 1 September 2024.
- ^ a b "Quarter-inch Administrative Areas Maps: Scotland, Sheet 3, 1968". National Library of Scotland. Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- ^ "No. 14590". The Edinburgh Gazette. 11 October 1929. p. 1188.
- ^ "The Lord-Lieutenants Order 1975", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 1975/428, retrieved 1 September 2024
- ^ "No. 23941". The Edinburgh Gazette. 23 February 1996. p. 423.
- ^ "Compositions calculator". The Elections Centre. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- ^ "Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, 1994 c. 39, retrieved 17 April 2023
- ^ "The Lord-Lieutenants (Scotland) Order 1996", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, SI 1996/731, retrieved 1 September 2024
- ^ "Land Mass Coverage Report" (PDF). Registers of Scotland. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
- ^ "Historical information from 1973 onwards". Boundary-Line support. Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 29 August 2024.
- ^ "ROSS AND CROMARTY: The Area of Ross and Cromarty in Scotland". British-towns.net. 15 July 2017. Archived from the original on 16 September 2017. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ^ "Stagecoach North Scotland - Black Isle and Easter Ross Travel Guide from 07 January 2019" (PDF). Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- ^ "Citylink Timetable - Glasgow to Ullpool" (PDF). Retrieved 23 June 2019.
Further reading
[edit]- D. Alston, Ross and Cromarty : a historical guide (Edinburgh : Birlinn, 1999 ISBN 1-874744-48-3), which, however, restricts itself to coverage of the mainland county;
- R. Bain, History of the Ancient Province of Ross (Dingwall, 1899);
- J. H. Dixon, Gairloch (Edinburgh, 1888);
- F. N. Reid, The Earls of Ross (Edinburgh, 1894);
- W. C. Mackenzie, History of the Outer Hebrides (Paisley, 1904).
External links
[edit]- Map sources for Ross and Cromarty